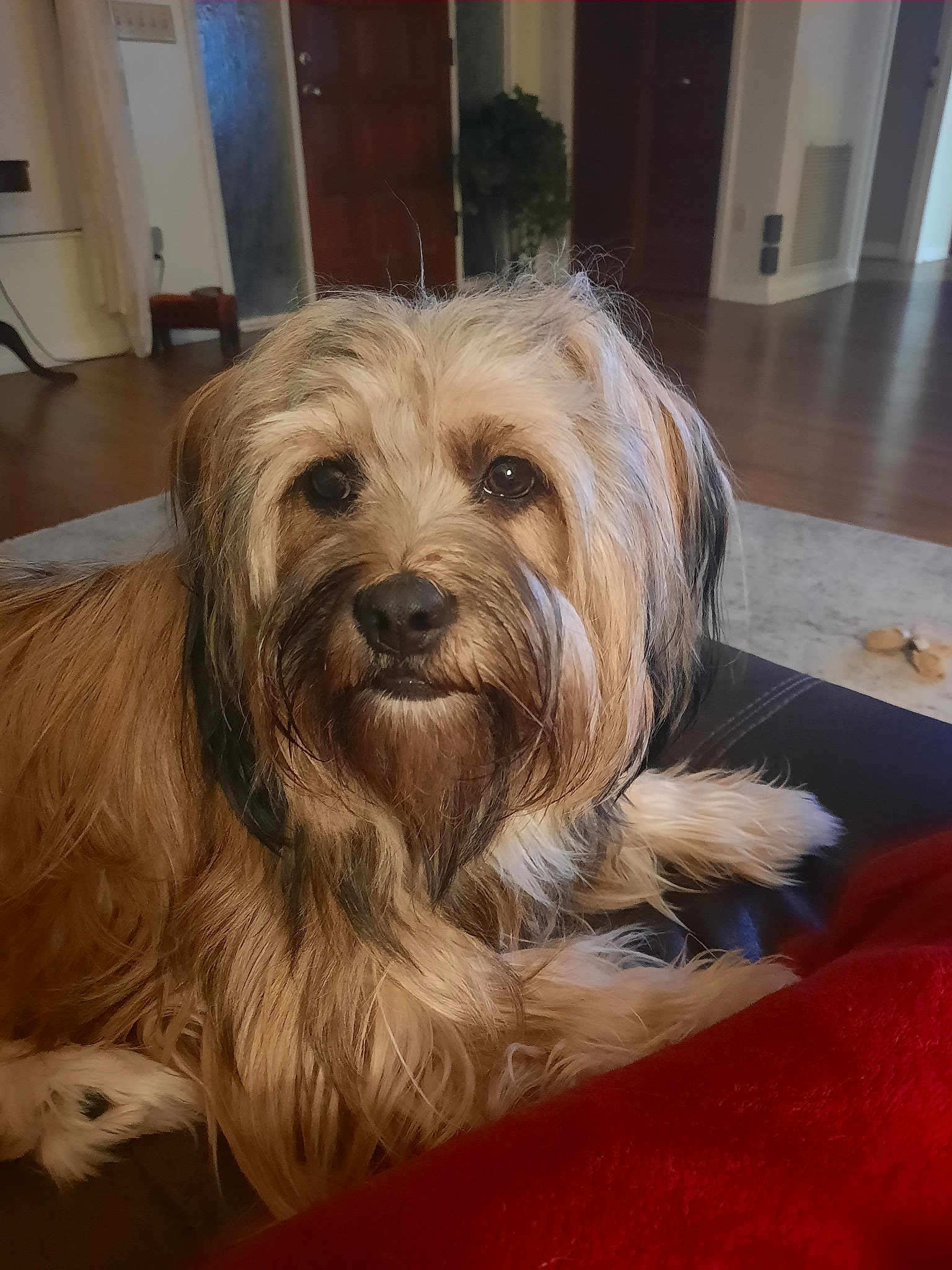
Did you know that the Tibetan Terrier isn't actually a terrier? This charming, medium-sized breed, known for its luxurious double coat and strong-willed nature, is more of a companion and sentinel than a typical terrier. Often considered the 'Holy Dog of Tibet,' this breed has lent its unique attributes and rich heritage to the world of canine companionship.
Personality and Behavior of the Tibetan Terrier
Tibetan Terriers are known for their distinct blend of playfulness and loyalty. They form strong bonds with their families and love to be part of household activities. Often described as affectionate and adaptable, these dogs thrive on human interaction and can be quite spirited.
In terms of behavior, Tibetan Terriers are known for their intelligence. This keen intellect means they can easily learn new commands and tricks, but it also means they require mental stimulation. A bored Tibetan Terrier might exhibit mischievous behavior, so it's important to keep them engaged with interactive toys and puzzle games.
Socially, they tend to be somewhat reserved with strangers. While not typically aggressive, they can be shy and may take time to warm up to new people. This protective nature makes them excellent watchdogs. Despite these traits, they usually get along well with other dogs and can be quite sociable in controlled environments.
Their playful nature extends to their compatibility with children. Tibetan Terriers are generally gentle and patient, making them good playmates for kids. However, like any breed, they should be supervised around very young children to ensure safe interactions.
A fascinating aspect of the Tibetan Terrier is their history as monastery dogs in Tibet, where they were often revered for their spiritual significance and were believed to bring good luck.
Meanings, History and Origins of the Name Tibetan Terrier
The name "Tibetan Terrier" is something of a misnomer. The breed does not belong to the terrier group; instead, it was so named by early Western travelers who noted its functional similarities to European terriers. Originating from the "Lost Valley" of Tibet, these dogs were not only watchdogs but also herders and companions, deeply woven into the fabric of Tibetan monastic life.
Historically, Tibetan Terriers were never sold but gifted as a mark of respect and goodwill. They were believed to hold spiritual significance, and owning one was thought to bring good fortune. Their presence in monasteries was seen as a blessing, and they served as companions to monks and assistance in daily tasks, further embedding them as sacred animals in their homeland.
The breed's history dates back over 2000 years, with documents and art depicting dogs that closely resemble today's Tibetan Terriers. Despite their ancient roots, they only began gaining international recognition in the early 20th century, primarily through efforts led by Dr. A.R.H. Greig, a British doctor who brought the first Tibetan Terrier to Europe.
Popularity of the Tibetan Terrier
Tibetan Terriers have a unique profile within the canine popularity charts. Their charming looks and well-rounded nature make them increasingly favored among dog enthusiasts. While not as commonly seen as some other breeds, they have carved out a niche for themselves among those who appreciate their unique qualities.
In English-speaking countries like the United States, the Tibetan Terrier enjoys moderate popularity. They are recognized by major kennel clubs, including the American Kennel Club (AKC), and often feature in dog shows and contests. Owners appreciate their manageable size and good-natured temperament, which make them suitable pets for both families and individuals.
Globally, the breed maintains a devoted following. In Europe, particularly the United Kingdom, Tibetan Terriers are well-regarded, with active breed clubs and enthusiasts who take pride in preserving and championing the breed's heritage. In their native regions, the breed continues to hold cultural and sentimental importance, although they remain primarily companion animals rather than working dogs.
Health and Care of the Tibetan Terrier
Tibetan Terriers are generally a healthy breed with a lifespan of 12-15 years. However, they are prone to certain genetic health issues that potential owners should be aware of. Common concerns include hip dysplasia, progressive retinal atrophy (PRA), and cataracts. Regular vet check-ups and genetic testing can help mitigate these risks.
Dietary needs for Tibetan Terriers are relatively straightforward but must be carefully managed. A balanced diet with high-quality dog food that meets their age, size, and activity level is essential. Owners should monitor their weight closely, as obesity can exacerbate joint issues and other health problems.
Grooming is a significant aspect of caring for a Tibetan Terrier. Their double coat requires regular brushing to prevent matting and tangling. It's also important to keep their ears clean and free from infections, and their nails trimmed. Regular baths help keep their coat healthy but should not be overdone to avoid stripping natural oils.
Exercise is another key component of their care. Tibetan Terriers are energetic and need daily walks and playtime to stay physically fit and mentally stimulated. They enjoy activities that challenge their intellect, making agility training and other interactive pursuits beneficial.
Training and Education of the Tibetan Terrier
Training a Tibetan Terrier can be both rewarding and challenging due to their intelligence and independent streak. They respond well to positive reinforcement techniques, such as treats, praise, and play. Consistency and patience are crucial, as the breed can sometimes be stubborn or willful.
Early socialization is important to prevent shyness and ensure a well-rounded adult dog. Exposing them to various sounds, sights, and experiences from a young age can help them become more adaptable and confident. Puppy classes and obedience training can provide structured settings for learning and socialization.
Common challenges include housetraining, which may require consistent routines and positive reinforcement. Crate training can be helpful in managing this process. Additionally, due to their tendency to form strong bonds with their families, Tibetan Terriers may experience separation anxiety. Gradual training to help them feel secure when alone is important.
Overall, the key to training a Tibetan Terrier lies in making the process enjoyable and engaging. Incorporating games, toys, and activities that stimulate their mind can keep them interested and willing to learn.
Choosing the right dog is a deeply personal decision that depends on various factors, including lifestyle, home environment, and individual preferences. For those who value a loyal, intelligent, and spirited companion, the Tibetan Terrier could be an excellent match. Their rich history and unique personality make them a delight to own and cherish.
The Tibetan Terrier's lasting significance lies in its unique blend of history, personality, and charm. At Pageant Dog, we have the pleasure of seeing many Tibetan Terriers participate in our photo contests, showcasing their beauty and character. If you're considering adding a dog to your family, the Tibetan Terrier offers a wonderful combination of companionship, security, and joy.